Agriculture and Farming in India
Archaeologists suggest that it was agriculture that changed the fate of humans from the rest of the animal kingdom. Thousands of years, or ago, the history of agriculture began with gathering wild grains for himself, research says that nascent farmers began to plant them (grains) around 11,500 years ago. Cattles like Pigs, sheep, and others were domesticated over 10,000 years ago.
Agriculture, a broad term covers farming too, but comparatively both the terms have similarities as well as differences on different aspects.
“Agriculture is the backbone of the Indian Economy”– said by Mahatma Gandhi six decades ago.
Meaning:
- From two Latin words Agri (field) and cultura (cultivation) makes the word ‘agriculture’
- ‘Farming‘ is derived from Latin noun of firma (contract or fixed agreement).
Agriculture redirect as 2 terms, as:
- ‘AGRICULTURE SCIENCE’ – An academic discipline of science.
- Agricultural science / agriculture degrees consist of listed courses through agriculture institute – Basic Science of Agriculture (Introductory Agriculture), Forestry, Agronomy, Horticulture, Plant Pathology, Fisheries (fish agriculture), Entomology, Agricultural Economics, Extension Education, Soil Science, Animal Husbandry, Genetics and Plant Breeding, Humanities, and Agricultural Engineering.
- ‘Farming’ – The practice/implementation of agriculture.
The practice of agriculture includes these broad areas –
Agricultural Practices / activities,
- Agriculture Sector includes four main sub-sectors, namely: 1) Crops. 2) Livestock (both production and animal health). 3) Fisheries and Aquaculture (including capture fisheries/fish agriculture). and 4) Forestry.
- STEPS FOR AGRICULTURE PRACTICES – Preparation of soil, Sowing, Adding Manure And Fertilizer, Irrigation, Protection from Weeds, Harvesting and Storage of Agricultural crops.
- Various agricultural crops include – Food Grains, Horticulture crops, Plantation crops, Medicinal & Aromatic Plants, etc.
Food grains
A. Cereals – Rice, Wheat, Jowar, Bajra, Ragi, Maize
B. Pulses – Peas, Tur, Gram, Red gram, Green gram, Black gram, Cow pea
Oilseeds – Groundnut, Soyabean, Sunflower, Safflower, Sesamum, Linseed
Cash crops – Sugarcane, Sugar-beet
Fibres – Cotton, Jute, Sunhemp
Drugs & Narcotics – Tobacco
Horticulture Crops
Vegetables – Bhendi, Bitter, Gourd, Cabbage, French Beans, Gavar
Root Crops – Potato, Bulb Crops, Onion
Fruits – Mango, Banana Sapota/Chickoo, Grapes, Orange, Pomegranate, Custard, Apple, Papaya, Guava, Limes & Lemons, Strawberry
Flowers – Rose, Carnation, Chrysanthemum, Gerbera, Gladiolus, Marigold, Tuberose, Tulip
Spices & Condiments – Black pepper, Cardamom, Vanilla, Ginger, Clove, Garlic, Nutmeg, Kokam, Turmeric, Curry Leaf
Plantation crops – Coconut, Arecanut, Cocoa, Cashewnut, Cinchona, Coffee, Tea Rubber
Medicinal & Aromatic Plants – Ocimum, Eucalyptus, Foxglove, Sarpagandha, Senna, Safed, Musli, Isubgol, Neem, Lavender, Sandalwood, Lemon grass, Citronella grass
Research and Development,
Food processing,
- Food processing is the transformation of agricultural products into food, or of one form of food into other forms. Food processing includes many forms of processing foods, from grinding grain to make raw flour to home cooking to complex industrial methods used to make convenience foods.
- During the last 6 years ending 2017-18, Food Processing Industries sector grew at an Average Annual Growth Rate (AAGR) of around 5.06 per cent. The sector constitutes as much as 8.83 per cent and 10.66 per cent of GVA in Manufacturing and Agriculture sector respectively in 2017-18 at 2011-12 prices.| Economic Survey |
Co-operation of the agriculture valued or relative products.
These areas are regulated under the Government of India through the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare (Ministry of Agriculture). The agriculture ministry is headed by Minister of Agriculture (Presently- Shri Narendra Sing Tomar), on the state level serving as – State Agriculture Ministers.
On the basis of the agricultural economy, The Planning Commission (Hindi: योजना आयोग, Yojana Āyog) recommended that agricultural planning to be done on the basis of agro-climatic regions/zones for holistic rural development, the country gained with natural resources so it has been broadly divided into 15 agro-climatic regions/zones (agricultural regions) based on agro-climatic features, particularly on:
- Soil (Soil type)
- Climate (including temperature and rainfall) and
- Resources availability (variation in rainfall & temperature and water)
India is a largely agrarian economy – with 52.1% of the population estimated to directly or indirectly employed in agriculture and allied activities/sectors in 2009-10. It also contributes a significant figure to the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) through agricultural products. Indian agricultural practices and allied agriculture sector activities have witnessed the green revolution including white revolution, yellow revolution, and the blue revolution and it succeeded only through agricultural extension programmes via agriculture and organic farming.
Agriculture, with its allied sectors, is the principal source of livelihood for more than half of the population, i.e. in the vast rural areas / agriculture sector of India. It provides the bulk of wage goods required by agribusiness companies or non-agriculture sectors and most of the raw agricultural products for the agribusiness / industries / allied sectors or agricultural services.
Simply the term – food system is used as nutritional values, food security, health, community growth & development and agriculture / farming , agricultural economics but the food system includes all processes from farmland till disposal of the food like the infrastructure involved in feeding a population: growing to use farm machinery, agricultural machinery, harvesting with farm equipment, processing, packaging of agricultural products as in agribusiness, transporting, marketing (agricultural economics), consumption, and disposal of food and food-related items.
| Economic Survey | 2010 The combined efforts of the Central Government, State Government’s agricultural extension programmes (agricoop) & the farming and agriculture community have succeeded in achieving record production of 244.78 million tonnes of foodgrains during 2010-11.

This record production farming and agriculture has been achieved by agriculture solutions and agricultural services to the farmer with agricultural extension programmes through the effective transfer of newly developed crop production technologies like farm tractors, agricultural machinery, agriculture equipment, agri center, information junctions to farmers under various crop development schemes, such as the [Agriculture MMP – Agriculture Mission Mode Project ], which is run under the direction of the Department of Agriculture & Cooperation ( agricoop ). Other causes behind record production include remunerative prices for various crops through enhanced minimum support prices on agricultural products for small scale farming produce.
High yielding agriculture crops and enhanced productivity mainly achieved through the effective transfer of newly developed crop production technologies under governmental schemes.
Various artificial innovative agricultural technologies are used to increase crop productivity with the least cost and natural resources like water in the irrigation process. To increase food production most popular companies/investors will invest in innovative agricultural technologies/startups because the demand for innovative farm technology is high, and when inventors show results, modern farmers have demonstrated a willingness to embrace those inventions and new techniques may be the future of agriculture like:-
- Sensor-based equipment ( Soil and Water )
- Weather Tracking/forecasting ( online weather services – meteorological department )
- Satellite Imaging ( real-time crop image )
- Pervasive Automation ( autonomous vehicles to reduces the operator’s workload )
- Vertical Farming ( Vertical farm technology can be used in urban areas or environment )
- robotic farming
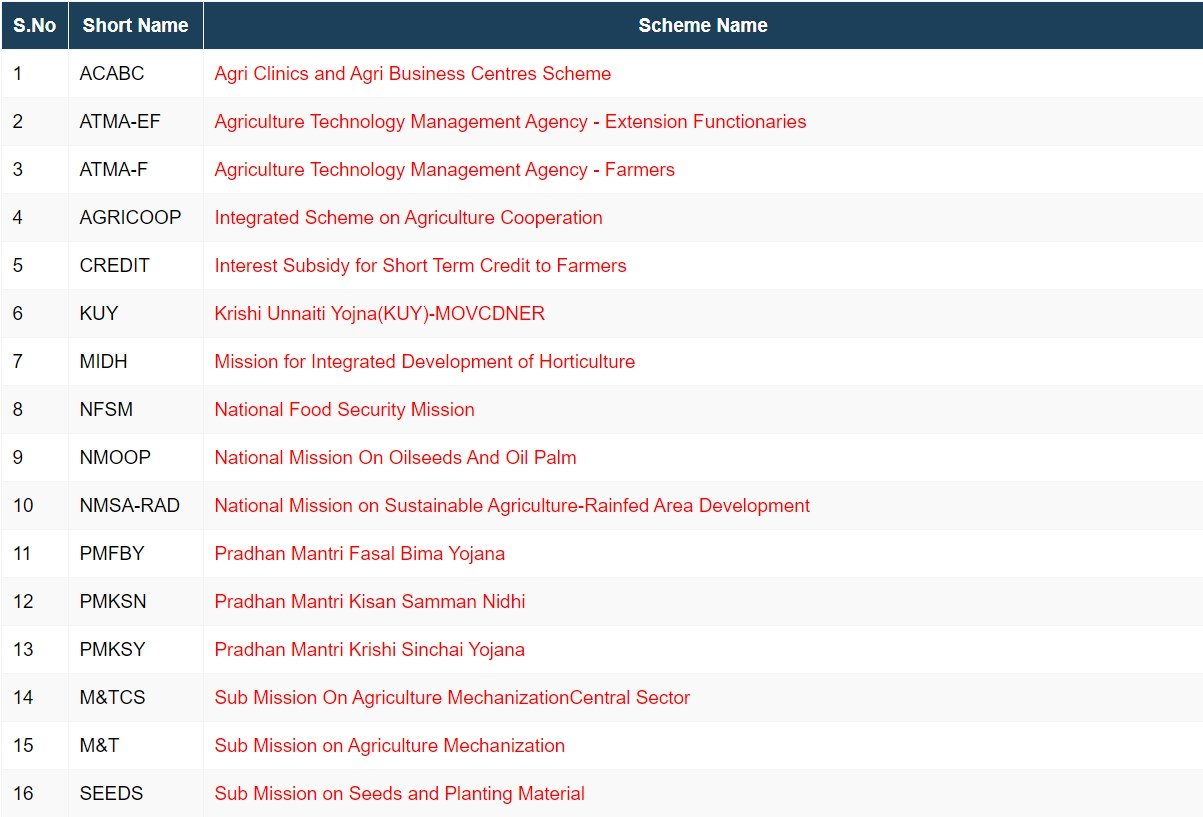
Important Government Schemes in the Agriculture sector
There are various agriculture development schemes / Agricultural programs / initiatives are the combined efforts of the Central Government, State Governments for farmers on central as well as state levels and a lot of information is available through online portals also some of them are given below:
Agriculture Development Schemes
- Pradhan Mantri Kisaan Maan-Dhan Yojana
- Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) Portal for Agriculture Schemes
- National Mission For Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA)
- National Agriculture Market (eNAM)
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi or PM-KISAN
- Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY)
- Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY)
- Gramin Bhandaran Yojna
- Livestock insurance Scheme
- Scheme on Fisheries Training and Extension
- National Scheme on Welfare of Fishermen
- Micro Irrigation Fund (MIF)
- Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana (PMKSY) (Har Khet ko Pani “Prime Minister Krishi Sinchayee Yojana”)
Online portals for farmers
National Level
- Scheme – Kisan Call Centres (KCCs)
Launched – on January 21, 2004.
Aim – to answer farmers’ queries on a telephone call in their own / regional language.
Locations – All the States and UTs ( 21 different locations )
Toll Free Number – 1800-180-1551
Kisan Call Centre agents known as Farm Tele Advisors (FTAs), who are graduate, agriculture degrees or above (i.e. PG or Doctorate) in Agriculture or allied sectors (Horticulture, Animal Husbandry, Fisheries, Poultry, Bee-Keeping, Sericulture, Aquaculture, Agricultural Engineering, Agricultural Marketing, Bio-Technology, Home Science, etc.) and possess excellent communication skills in respective local language.
- Farmers Portal { One Stop Shop For Farmers }
A farmer can be able to get all relevant information on specific subjects/queries around his village/block /district or state. This information will be delivered in the form of text, SMS, email and audio/video in the language, he or she can understand.

- The Agriculture Centre (agri centers)
- A private non-official Society
- interact on agricultural issues, and
- issues related to performing arts, specially traditional, folk and rural arts
- mKisan Portal
- Agricultural extension services in India have gonna changes through the Green Revolution, so the divergent needs of the farmers also changed in the field of sustainable agriculture /organic farming.
- Specific requirements of the farmers based on their crops, agro climatic situation and farm machinery etc., so they can solve out with this mKISAN Portal with agricultural solutions regarding there queries, information about smart farming.

Worldwide (World Agriculture Platforms)

e-agriculture
In 2003 and 2005, the World Summit on the Information Society uses the term “e-agriculture” Globally agriculture online community the Community of Practice (CoP) exchange information, ideas, and resources related to the use of information and communication technologies (ICT) for sustainable agriculture and rural development.
Source: | Wikipedia | FAO | Indiatoday | ICAR |
