Only at night does the tuberose flower blossom, and this is the only time when it is active. As a result, they are also known as “Night Queen” or “Mistress of the Night.” The flower shoot adds elegance to the plant, and when it swings with the breeze, it releases a fresh, delicious aroma that energizes all of your senses!
This Plant is most usually associated with weddings. It is, in fact, highly popular and reasonably priced among perfumers. It’s flowers are called ‘Tuberose’ because of its tuberous root system. Tuberose essential oil is commercially accessible, however it is highly rare and difficult to come by.
The leaves look like grass stems and grow in clusters. The plant grows from the mother plant’s rhizomes, and different plants sprout from the original plant’s side. Rajnigandha (रजनीगंधा), Nishigandha, and Sword Lilly are some of its other names.
Uses of Rajnigandha Flower:
Decorative Uses and Other
- Garlands, floral ornaments, bouquets, and buttonholes are all made using them.
- Cut flowers for table decoration can be made from the long flower spikes.
- Tuberose oil, which is used in high-end fragrances and cosmetics, is derived from the blooms, which have a pleasant scent.
- Additionally, fragrant flowers, as well as stimulants or sedatives, are added to the popular chocolate beverage, which can be served cold or hot.
Medicinal uses:
- The alkaloid lycorine, which produces vomiting, is said to be present in the bulbs.
- The bulbs are rubbed with turmeric and butter before being administered as a paste on newborns’ red pimples.
- The powdered version of dried tuberose bulbs is used as a gonorrhoea treatment.


If you are interested to plant in your garden or Pot you can visit these Links to grow yourself.
Plant Overview to Plant in Your Garden
| Rajnigandha Flower In English | Tuberose |
| Scientific Name | Polianthes tuberosa L. |
| Family | Amaryllidaceae |
| Common Name | Tuberose |
| Hindi Name | (रजनीगंधा) |
| Common Name | Mexican tuberose, Tuberose, Rajanigandha |
| Height | 2 to 3 feet |
| Flower Colour | White |
| Bloom Time | Summer, Autumn |
| Difficulty Level | Easy to grow |
| Sunlight | Full Sun to Partial sun |
| Watering | Moderately |
| Soil | Well-drained loam soil |
| Temperature | 21 to 30 degrees C |
| Fertilizer | Apply any organic fertilizer. |
Origin and History Rajnigandha Plant
Rajnigandha Plant (रजनीगंधा) that originated in Mexico and spread around the world during the 16th century. Tuberose is thought to have arrived in India via Europe in the 16th century.
Read More: Wheat Crop Cultivation
Area and Distribution of Tuberose
Tuberose is widely grown in France, South Africa, North Carolina, the United States, and many other tropical and subtropical regions, including India. The country’s entire tuberose cultivation area is believed to be around 3,000 hectares at the moment.
Tuberose is grown commercially in Mysore, Devanhalli taluk (Karnataka), East Godavari, Guntur, Chitoor, Krishna, Distt. (Andhra Pradesh), Coimbatore and Madurai (Tamil Nadu), Pune, Thane, Sangli (Maharashtra), Bagnen, Kolaghat, Midnapore, Panskura, Ranaghat, Krishnanagar, and Krishnanagar, and (West Bengal).
Botanical Description of Nishigandha / Rajnigandha
- Tuberose (रजनीगंधा) is a bulbous, perennial, half-hardy plant.
- Rajnigandha’, ‘Nishigandha‘, and ‘Sword Lilly’ are some of its other names.
- Scales and leaf bases make up bulbs, while the stem is hidden within the scales.
- The majority of the roots are adventitious and shallow.
- Flowers are fragrant, waxy white, and about 25 mm long, with a funnel-shaped perianth.
- The number of stamens is six, the ovary is three locular, the ovules are numerous, and the fruits are capsule.
Climatic Requirement of Rajanigandha
Tuberose (रजनीगंधा) also is grown commercially in India in warm, humid climates with average temperatures ranging from 16° to 30°C. Tuberose can also be found in mountainous locations with elevations of 1200 to 1500 metres.
The two key factors that determine whether or not production increases or decreases are humidity and temperature. Temperatures above 40°C cause the length of the spike to shorten and the quality of the flowers to deteriorate.
Similarly, a drop in temperature or the occurrence of frost harms the plant and its blossoms. It enjoys a sunny location and should not be cultivated in a shaded or semishady location since the flower output will be dramatically reduced.
Long-day exposure improves vegetative growth as well as the early emergence of the first flower spike and extends the length of the flower spike, despite the fact that tuberose is not technically photosensitive. Growth and flowering were aided by a 16-hour day.
Soil Requirement for Rajnigandha Plantation
Tuberose (रजनीगंधा) should be planted in a well-drained area because it cannot survive even a brief period of water logging.
Tuberose may be grown in a variety of soils, from light sandy to clay, including those with high salinity and alkalinity.
Tuberose cultivation thrives in fertile loamy and sandy soils with a pH range of 6.5 to 7.5 with good aeration and drainage.

Varieties of Tuberose/ Rajnigandha
There are four types of tuberose-
Single:
- With a single whorl of corolla and a strong aroma, these flowers are mostly utilised for concrete extraction.
- Concrete content was found to be between 0.08 and 0.11 percent.
- Floral ornaments are made from loose flowers. The most common kinds include Single, Kalyani Single, Shringar, Prajwal, Rajat Rekha, Hyderabad Single, and Culcutta Single.
Shringar:
- This variety is the result of a cross between ‘Single x Double’ and ‘Single x Double’.
- On robust spikes, it bears a single type of flower.
- The bloom bud has a reddish hue to it.
- Florets are more attractive and larger than ‘Calcutta Single.’
- Meloidogyne incognita worm resistant. Loose blooms can be used to make garland, while spikes can be used as cut flowers.
- The Hybrid’s loose flower yield is roughly 15,00 kh/ha per year, which is 40% more than ‘Calcutta or Mexican Single,’ and the concrete content is comparable to Mexican Single.
- Farmers and the fragrance industry prefer Shringar.
Semi-double:
It has two to three whorls of petals and is utilised for both concrete extraction and cut flower.
Double:
Varieties having more than three whorls belong to this category. They’re mostly utilised for bouquets and cut flowers. Double, Kalyani Double, Swarn Rekha, Hyderabad Double, Culcutta Double, Vaibhav, and Suvasini are the most common kinds.
Vaibhav:
- The hybrid with semi-double flowers on medium spikes is the result of a cross between ‘Mexican Single’ and IIHR – 2.
- ‘Suvasini’ and ‘Local Double’ have pinkish flower buds, whilst ‘Suvasini’ and ‘Local Double’ have greenish flower buds.
- Flowers are white in colour.
- When compared to ‘Suvasini,’ the spike yield is 50% higher.
- As a result, it is suggested for use as a cut flower.
Suvasini:
- The cross of ‘Single’ and ‘Double’ produced a multi-whorled variation.
- Pure white flowers with a long spike are bold and large.
- The best use for spikes is as a cut flower.
- Suvasini produced a 25% higher yield than cv. Double.
- IIHR, Bangalore has lately developed two additional new tuberose types, Prajwal and Vaibhav.
Prajwal:
- This hybrid is a cross of ‘Shringar’ and ‘Mexican Single,’ with single type blooms on tall stiff spikes.
- The flower buds are pinkish-white in colour, while the flowers are white.
- In comparison to ‘Local Single,’ the individual flowers are much larger.
- It produces 20% more loose flowers than the ‘Shringar’ variety.
- Both loose flowers and cut flowers are recommended.
Variegated:
Leaves with white/yellow streaks are evident in these cultivars. By using gamma irradiation, the National Botanical Research Institute in Lucknow has created two variegated types, Rajat Rekha and Swarn Rekha.
Rekha Rajat:
- With a silvery white streak down the centre of the leaf blade, this is a single flowered variety.
- It’s a mutation that resulted from irradiating single-flowered cultivar bulbs.
- The amount of concrete in the sample was found to be 0.089 percent.
Rekha Swarna:
- Golden yellow steaks run along the leaf margins in this double flowered variety.
- It’s a gamma ray-induced mutant with a mutation in chlorophyll production that causes a change in leaf colour.
- The amount of concrete in the sample was found to be 0.062 percent.
Field Preparation and Sowing
Preparation of field:
2-3 ploughings (45 cm) should be used to plough the field deep enough to achieve a decent tilth, and the field should be thoroughly manured. Weeds and insect pests are killed by leaving the field for 15 days. At a rate of 50 tonnes per hectare, well-rotten cow dung or farmyard manure should be integrated into the soil. Following field preparation, appropriate-sized plots should be prepared.
Spacing:
Bulbs are planted at a depth of 4-6 cm with a spacing of 30×20 cm or 20×20 cm. For a one-acre tuberose plantation, 40,000-50,000 bulbs are required.
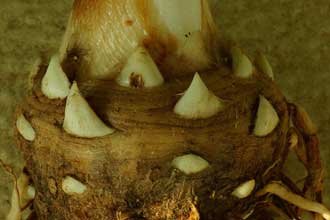
Propagation:
Bulbs are used to propagate Rajni Gandha Flower. Bulbs with a diameter of 1.5 to 2.5 cm are generally good for planting. For one hectare of planting, around 1.25-1.5 lakh bulbs (800-900 kg) are required.
Season:
Planting takes place on the plains from March to April, and in the hills from April to May.
Treatment of seeds
- These bulbs are cleaned completely and then treated for 30 minutes with Bavistin (0.2 percent).
- The resting period can be broken by dipping the bulbs in a 4 percent thiourea solution. Pre-plant bulb storage at 10°C for 30 days to boost plant development, spike and bloom yield.
- Pre-planting treatment of bulbs with GA3, etherel, or thiourea stimulated early flowering and resulted in the most longer spikes with the most florets.
If you are interested to plant in your garden or Pot you can visit these Links to grow yourself.
- Rajnigandha, Tuberose – Bulbs :- Amazon
- Rajnigandha, Tuberose – Bulbs Double Variety ( Big Bundle Pack ) :- Buy Now
FAQ (Frequently Asked Question about Rajnigandha)
What is the use of Rajnigandha flower?
Economic and Industrial application(s): Rajnigandha is a well-known for Pan masala but this plant (Polianthes tuberosa) best known for its usage in bouquets and huge demand of essential oil(s). Rajnigandha essential oil is used in a wide range of Ayurvedic remedies, Sweets, Drink, Dental care, and Mouth freshener or Mouthwash.


